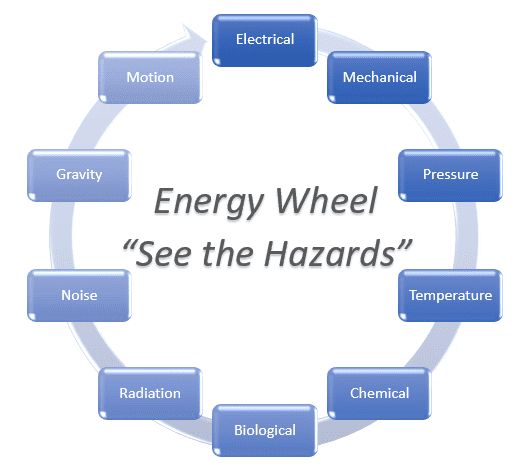
five basic hazard control strategies in the hierarchy of controls

The principle is that it's more effective to eliminate the hazard than to control exposure to the hazard.
ANSI ASSP Z10-2012, Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems, encourages employers to use the hierarchy of hazard controls.
Administrative controls Reduce exposure to the hazard through training, policies, procedures, practice, etc..
The idea behind this hierarchy is that the control methods at the top of the list are potentially more effective and protective than those at the bottom.
Following the hierarchy leads to the implementation of inherently safer systems, ones where the risk of illness or injury has been reduced..
Redesigning or replacing equipment or machinery may be expensive, and remember the average direct and indirect cost of lost-work injury can be more than $50,000 easily more than $1 million to close fatality claim..
One of the important goals of JHA is to turn the dangerous step into safe step that does not require safety precautions.
we'll need to manage exposure to the hazard with safety precautions.
Methods to eliminate or reduce employee exposure to hazards include placing warning signs, tape, cones, etc., to make workers aware of the hazard within step. developing new policies, procedures, and practices to reduce duration of exposure. revising work schedules to reduce the duration of exposure. training..
PPE is acceptable as in the following circumstances when engineering controls are not feasible or do not eliminate the hazard while engineering controls being developed when safe work practices do not provide sufficient protection during emergencies when engineering controls may not be feasible.
Read more
ANSI ASSP Z10-2012, Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems, encourages employers to use the hierarchy of hazard controls.
Administrative controls Reduce exposure to the hazard through training, policies, procedures, practice, etc..
The idea behind this hierarchy is that the control methods at the top of the list are potentially more effective and protective than those at the bottom.
Following the hierarchy leads to the implementation of inherently safer systems, ones where the risk of illness or injury has been reduced..
Redesigning or replacing equipment or machinery may be expensive, and remember the average direct and indirect cost of lost-work injury can be more than $50,000 easily more than $1 million to close fatality claim..
One of the important goals of JHA is to turn the dangerous step into safe step that does not require safety precautions.
we'll need to manage exposure to the hazard with safety precautions.
Methods to eliminate or reduce employee exposure to hazards include placing warning signs, tape, cones, etc., to make workers aware of the hazard within step. developing new policies, procedures, and practices to reduce duration of exposure. revising work schedules to reduce the duration of exposure. training..
PPE is acceptable as in the following circumstances when engineering controls are not feasible or do not eliminate the hazard while engineering controls being developed when safe work practices do not provide sufficient protection during emergencies when engineering controls may not be feasible.
Read more
Report
Related items: